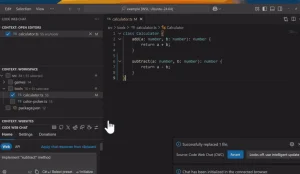
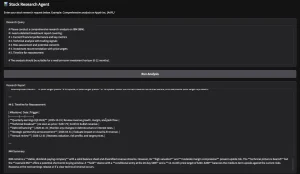
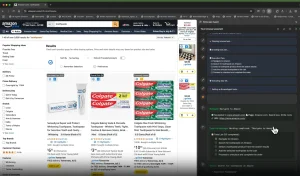
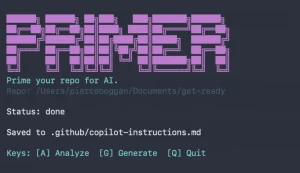
Crush is an open-source command-line AI coding agent that helps you write, debug, and understand code using your preferred large language model.
Developed by Charm, a company known for making command-line interfaces more “glamorous,” Crush provides a powerful and customizable AI coding experience.
It stands as a strong alternative to other command-line tools like Gemini CLI, Claude Code, OpenAI CodeX, and more.
Features
- Multi-Model Support: Switch between OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, Groq, and other providers within the same session.
- Session Management: Maintain separate contexts for different projects with persistent conversation history.
- LSP Integration: Leverage Language Server Protocol for enhanced code understanding, just like modern editors.
- MCP Protocol Support: Extend functionality through Model Context Protocol servers using stdio, HTTP, or Server-Sent Events.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Works on macOS, Linux, Windows (PowerShell and WSL), FreeBSD, OpenBSD, and NetBSD.
- Flexible Configuration: Customize providers, models, and permissions through JSON configuration files.
- Built-in Logging: Track all interactions with detailed logs stored locally for debugging and review.
See It In Action
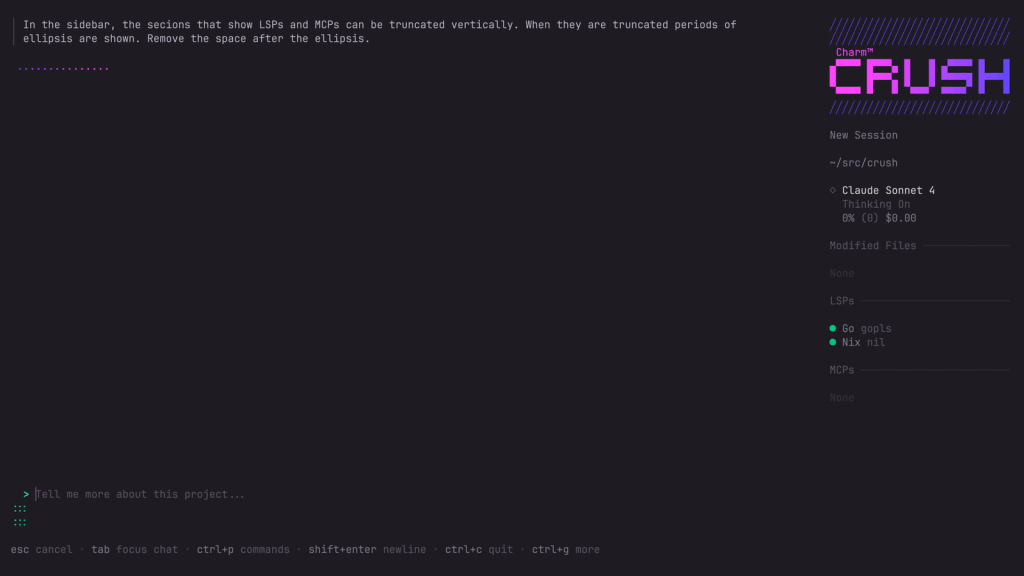
Installation
You can install Crush using several package managers, or by downloading the binary directly. Choose the method that best fits your system.
Homebrew (macOS & Linux)
If you’re on macOS or a Linux distribution that uses Homebrew, you can install Crush with a single command:
brew install charmbracelet/tap/crushNPM
For those in a Node.js environment, you can install it globally using npm. This works across Windows, macOS, and Linux.
npm install -g @charmland/crushLinux Distributions
Crush provides dedicated repositories for popular Linux package managers.
Arch Linux
Arch users can find Crush in the Arch User Repository (AUR). Use your favorite AUR helper, like yay, to install it:
yay -S crush-binDebian / Ubuntu
For Debian-based systems, you need to add the Charm repository and its GPG key before installing:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://repo.charm.sh/apt/gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/charm.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/charm.gpg] https://repo.charm.sh/apt/ * *" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/charm.list
sudo apt update && sudo apt install crushFedora / RHEL
Similarly, for Fedora, RHEL, or CentOS, add the Charm repository to your system:
echo '[charm]
name=Charm
baseurl=https://repo.charm.sh/yum/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://repo.charm.sh/yum/gpg.key' | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/charm.repo
sudo yum install crushNix
Nix users can run Crush directly or install it declaratively. To run it without a permanent installation, use:
nix run github:numtide/nix-ai-tools#crushGo Install
If you have a Go development environment set up, you can build and install Crush from the source:
go install github.com/charmbracelet/crush@latestManual Download
You can also download pre-compiled binaries or packages (in .deb and .rpm formats) directly from the Crush GitHub releases page.
Usage
1. After installation, launch Crush by typing crush in your terminal. The CLI will prompt you to enter an API key for your preferred AI provider. You can use keys from Anthropic, OpenAI, Google Gemini, Groq, or OpenRouter.
2. Once configured, Crush works like an interactive chat session where you can request code generation, ask questions about your project, or seek help with debugging. The CLI maintains context throughout your session, remembering previous conversations and code snippets.
3. Create a .crush.json file in your project directory or home folder to customize behavior. This includes setting up multiple providers, configuring LSP servers for better code understanding, or adding MCP servers for extended functionality.
{
"$schema": "https://charm.land/crush.json",
"lsp": {
"Go": {
"command": "gopls"
}
}
}Pros
- Provider Flexibility: Switch between different AI models mid-conversation while preserving context.
- Native Terminal Experience: No need to leave your command-line workflow for AI assistance.
- Open Source: Free to use with transparent development on GitHub.
- Full Platform Support: Works across all major operating systems and terminal environments.
- Developer-Focused: Built specifically for coding tasks with LSP integration and project-aware context.
Cons
- API Key Requirements: Requires paid API access to major language model providers.
- Command-Line Only: No graphical interface for users who prefer visual interactions.
- Learning Curve: Configuration options may overwhelm users who want simple plug-and-play functionality.
- Session Management: Multiple project contexts require manual switching and organization.
Related Resources
- Anthropic API Documentation: https://docs.anthropic.com – Setup guide for Claude integration.
- Charm Discord: https://charm.land/discord – Community support and discussions about Crush and other Charm tools.
- Catwalk Repository: https://github.com/charmbracelet/catwalk – Community-maintained model configurations for extending Crush compatibility.
FAQs
Q: Is Crush completely free to use?
A: The Crush application itself is free and open-source. However, it uses third-party Large Language Models (LLMs) to function, and you will be responsible for any costs associated with the API usage from providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, or Google.
Q: How does Crush compare to GitHub Copilot in the terminal?
A: Both provide AI coding assistance in the terminal, but they have different approaches. GitHub Copilot is more focused on inline code completion and suggestions. Crush acts more like a conversational AI agent within a session, where you can ask it to perform broader tasks, modify files, and manage a project’s context.
Q: Can I use local LLMs with Crush?
A: Yes. You can configure Crush to connect to any OpenAI-compatible API. If you are running a local LLM that exposes such an endpoint (for example, with Ollama), you can point Crush to it in your configuration file.
Q: Does Crush store my code or conversations anywhere?
A: Crush stores logs locally in your project directory under ./.crush/logs/crush.log. No data is sent to Charm’s servers beyond what’s necessary for the tool to function.
Q: Can I customize which tools Crush can execute automatically?
A: Yes, you can whitelist specific tools in your configuration file to execute without permission prompts. For complete automation, use the --yolo flag, though this requires careful consideration of security implications.