Nanobot is a free, open‑source personal AI assistant developed by the Data Intelligence Lab at the University of Hong Kong.
It delivers the core functionality of a modern AI agent, like chat, task execution, scheduling, and tool integration, in roughly 4,000 lines of Python code. That’s about 99% smaller than heavyweight frameworks like OpenClaw (formerly Clawdbot).
The project calls itself an “ultra‑lightweight Clawdbot alternative,” and that’s exactly what it is: a minimal, readable codebase that lets you spin up a working assistant in under a minute.
You can chat with it via Telegram or WhatsApp, connect it to your favorite LLM (including local models), and extend it with custom skills.
If you’ve ever wanted a JARVIS‑like helper without the complexity of a half‑million‑line monolith, nanobot is worth a look.
Features
- Ultra-Lightweight: Nanobot runs on approximately 4,000 lines of Python code compared to OpenClaw’s 430,000+ lines.
- Multiple LLM Providers: The assistant works with OpenRouter, Anthropic Claude, OpenAI GPT, Groq, Google Gemini, and local vLLM servers.
- Chat Platform Integration: Connect nanobot to Telegram or WhatsApp. Both channels use allowlist security to restrict access.
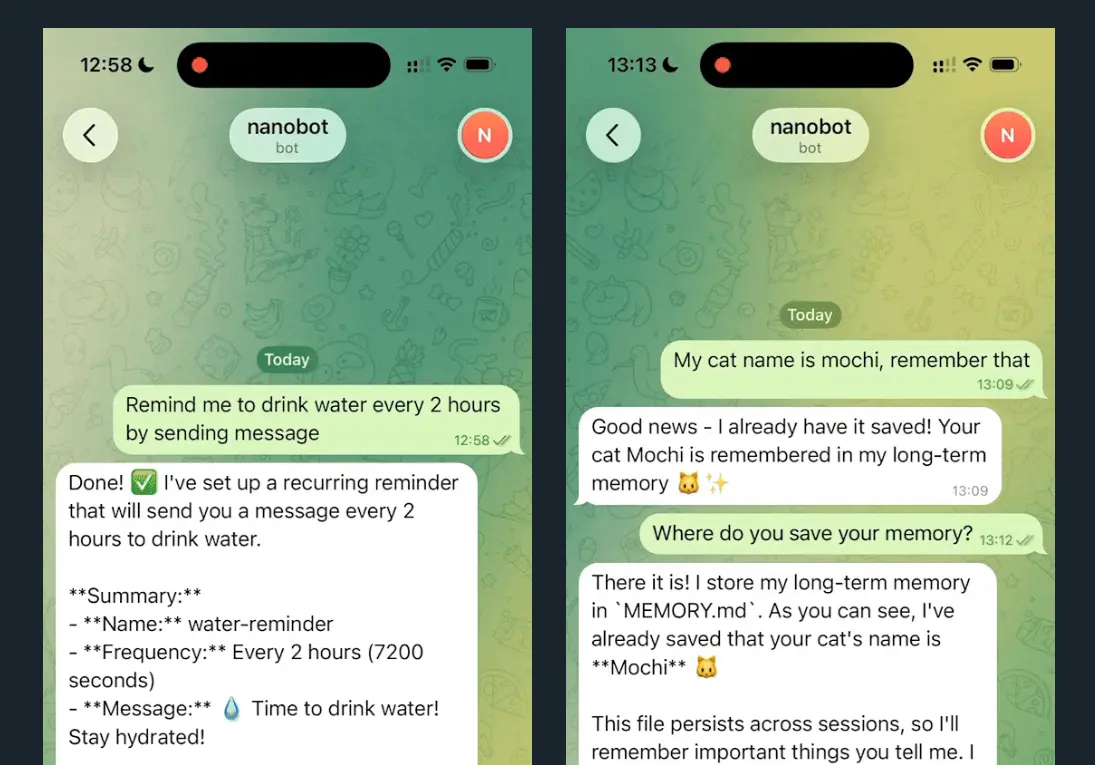
- Task Scheduling with Cron: Create recurring tasks using standard cron syntax or interval-based scheduling.
- Voice Transcription: Groq’s Whisper integration converts Telegram voice messages to text automatically.
- Local Model Support: Run nanobot with your own models using vLLM or any OpenAI-compatible inference server.
- Modular Skills System: Extend functionality through bundled skills (GitHub, weather, tmux) or create custom skills.
- Persistent Memory: The agent maintains conversation context and user preferences across sessions through its memory module.
- Real-Time Web Search: Optional Brave Search API integration provides current information beyond the LLM’s training cutoff.
See It In Action
Nanobot vs. OpenClaw
| Aspect | Nanobot (HKUDS) | OpenClaw (Original) |
|---|---|---|
| Codebase Size | ~4,000 lines | 400,000+ lines |
| Language Core | Python | Multi-language (TS/Go/CLI) |
| System Footprint | Ultra-low (Micro-kernel) | Heavy (Monolith) |
| Installation | Single command (pip/uv) | Multi-step (Docker/VPS/Nix) |
| Auditability | High (Read in 1 hour) | Low (Complex abstractions) |
| Plugin System | Manual/Minimalist | Massive (ClawHub) |
| Primary User | Researchers and Developers | Power users and Automators |
Nanobot functions as a direct response to the complexity of OpenClaw. It targets users who prioritize control and speed. OpenClaw provides a wide range of automated features. This comes at the cost of a massive codebase and high resource consumption.
- Resource Efficiency: Nanobot runs on modest hardware. This allows you to host it on a basic home server or a Raspberry Pi.
- Architectural Transparency: The code remains readable. You can modify the agent loop because the structure is flat and modular.
- Feature Scope: OpenClaw includes proactive browser automation and a canvas workspace. Nanobot focuses on the core agent-tool interaction loop.
- Speed: Nanobot starts instantly. It avoids the overhead associated with large multi-language frameworks.
Use Cases
- Market Research and Analysis: Set up scheduled jobs to fetch market data, analyze trends, and deliver daily reports through Telegram.
- Software Development Assistant: Deploy nanobot locally with your preferred LLM to help write code, debug issues, and manage GitHub repositories through the built-in GitHub skill.
- Daily Routine Automation: Create cron jobs for morning briefings, meeting reminders, or evening summaries.
- Personal Knowledge Base: The memory system stores important information from conversations. You can ask the agent to recall details from previous interactions without repeating context.
- Privacy-Focused AI Assistant: Run nanobot entirely locally using vLLM with open-source models like Qwen. Your data never leaves your machine.
How to Use Nanobot
Table Of Contents
Installation
You have three installation options. From source gives you the latest features and works best for development:
git clone https://github.com/HKUDS/nanobot.git
cd nanobot
pip install -e .The uv tool installer provides fast, stable installation:
uv tool install nanobot-aiPyPI offers the standard Python package approach:
pip install nanobot-aiInitial Setup
Run the onboard command to initialize your configuration:
nanobot onboardThis creates ~/.nanobot/config.json. Open the file and add your API keys. OpenRouter requires an API key from openrouter.ai/keys. Brave Search is optional but needed for web search capabilities.
{
"providers": {
"openrouter": {
"apiKey": "sk-or-v1-xxx"
}
},
"agents": {
"defaults": {
"model": "anthropic/claude-opus-4-5"
}
},
"webSearch": {
"apiKey": "BSA-xxx"
}
}Using Local Models
Start your vLLM server:
vllm serve meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct --port 8000Update your config to point to the local endpoint:
{
"providers": {
"vllm": {
"apiKey": "dummy",
"apiBase": "http://localhost:8000/v1"
}
},
"agents": {
"defaults": {
"model": "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"
}
}
}Chat Interface
Send a single message:
nanobot agent -m "What is 2+2?"Start interactive mode:
nanobot agentTelegram Setup
Open Telegram and search for @BotFather. Send /newbot and follow the prompts. Copy the token you receive.
Add Telegram configuration:
{
"channels": {
"telegram": {
"enabled": true,
"token": "YOUR_BOT_TOKEN",
"allowFrom": ["YOUR_USER_ID"]
}
}
}Get your user ID from @userinfobot on Telegram. Start the gateway:
nanobot gatewayWhatsApp Setup
WhatsApp requires Node.js 18 or higher. Link your device first:
nanobot channels loginScan the QR code using WhatsApp → Settings → Linked Devices.
Configure WhatsApp in config.json:
{
"channels": {
"whatsapp": {
"enabled": true,
"allowFrom": ["+1234567890"]
}
}
}Run two terminals simultaneously:
Terminal 1:
nanobot channels loginTerminal 2:
nanobot gatewayScheduled Tasks
Add a daily job at 9 AM:
nanobot cron add --name "daily" --message "Good morning!" --cron "0 9 * * *"Add an interval-based job (every hour):
nanobot cron add --name "hourly" --message "Check status" --every 3600List all jobs:
nanobot cron listRemove a specific job:
nanobot cron remove <job_id>Docker Deployment
Build the container:
docker build -t nanobot .Initialize configuration:
docker run -v ~/.nanobot:/root/.nanobot --rm nanobot onboardEdit the config file on your host machine:
vim ~/.nanobot/config.jsonRun the gateway:
docker run -v ~/.nanobot:/root/.nanobot -p 18790:18790 nanobot gatewayThe -v ~/.nanobot:/root/.nanobot flag mounts your local config directory into the container for persistence.
CLI Command Reference
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
nanobot onboard | Initialize config and workspace |
nanobot agent -m "message" | Send single message to agent |
nanobot agent | Start interactive chat mode |
nanobot gateway | Launch chat platform gateway |
nanobot status | Display system status |
nanobot channels login | Link WhatsApp device (QR code) |
nanobot channels status | Show channel connection status |
nanobot cron add | Create scheduled task |
nanobot cron list | Display all scheduled tasks |
nanobot cron remove <id> | Delete scheduled task |
Pros
- Privacy-Focused: Local model support via vLLM keeps data off external servers.
- Fast Deployment: You can go from zero to a working agent in under two minutes.
- Low Resource Usage: Nanobot runs comfortably on modest hardware.
- Research Friendly: The clean module structure (agent, skills, channels, providers) makes extending functionality straightforward.
Cons
- Limited Pre-built Skills: The ecosystem is smaller than OpenClaw’s.
- Technical Barrier: The tool relies heavily on CLI and JSON configuration.
Related Resources
- OpenRouter: Unified API access to multiple LLM providers, including Claude, GPT, and Gemini. Recommended for nanobot deployment.
- vLLM Documentation: Learn how to set up local inference servers for privacy-focused deployments.
- Brave Search API: Enable real-time web search capabilities in your nanobot instance.
- Telegram Bot Tutorial: Official guide for creating and managing Telegram bots.
More OpenClaw Alternatives
- NanoClaw: Lightweight, Secure OpenClaw Alternative.
FAQs
Q: Can I run nanobot completely offline?
A: Yes. Install nanobot locally, set up a vLLM server with an open-source model like Llama, and configure your agent to use the local endpoint. Your conversations stay on your machine. Web search won’t work offline, but core agent functionality remains intact.
Q: How does nanobot compare to OpenClaw in terms of performance?
A: Nanobot starts faster and uses fewer resources because of its smaller codebase. OpenClaw offers more features like browser automation and platform integrations, but requires more powerful hardware and longer startup times.
Q: What happens if my API key runs out of credits?
A: The agent stops processing requests when API credits expire. You’ll see error messages in the CLI. Add credits to your OpenRouter or other provider account to resume operation. Local vLLM deployments don’t have this limitation.
Q: Can I use multiple LLM providers simultaneously?
A: The current configuration supports one default model per agent. You can switch providers by changing the model parameter in config.json, but simultaneous multi-provider operation isn’t supported out of the box.
Q: What security measures should I take when deploying nanobot?
A: Use the allowFrom arrays in channel configurations to restrict access to specific user IDs or phone numbers. Keep your API keys in config.json secure with proper file permissions (chmod 600). For production deployments, run nanobot inside Docker containers and limit network exposure to necessary ports only.