Mistral Vibe is a free, open-source command-line AI coding agent that allows you to interact with your codebase using natural language.
Mistral AI released this coding assistant to provide a transparent, customizable alternative to closed-source coding agents like Claude Code.
You can use it to automate repetitive coding tasks, debug errors by piping logs directly to the agent, or modernize legacy systems directly in your local terminal.
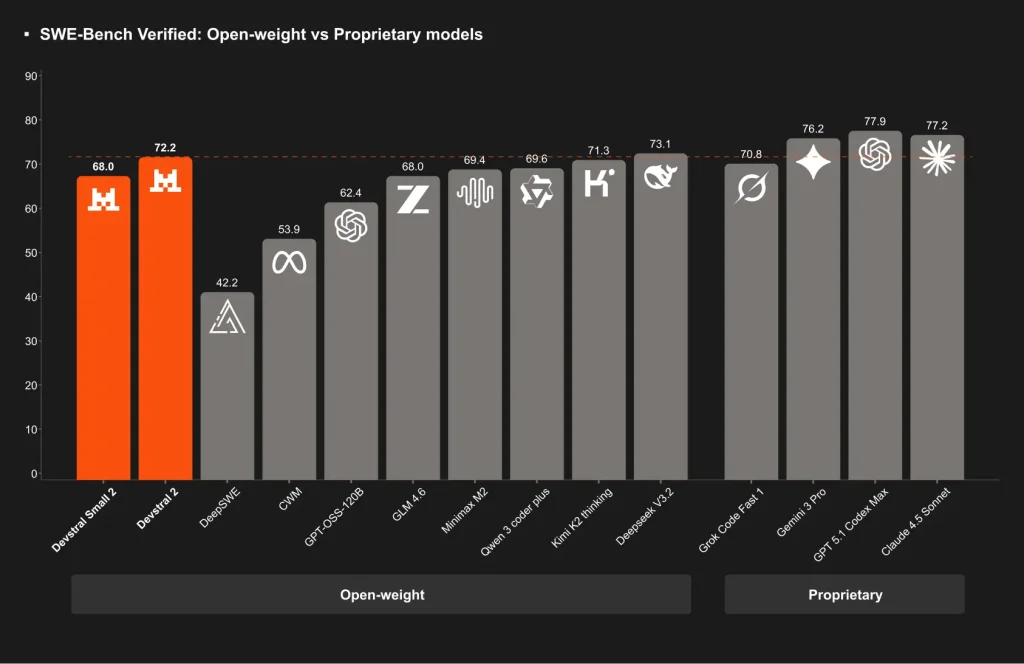
Mistral Vibe is powered by Devstral 2, a 123B-parameter coding model developed by leading AI model provider Mistral AI. It achieves a 72.2% score on SWE-bench Verified and holds a significant 42.8% win rate against DeepSeek V3.2 in human evaluations.
Mistral Vibe is currently 100% free to use. This is possible because Mistral AI is offering the Devstral 2 API at no cost during its initial launch period. This is an excellent time to test the tool without incurring the high usage costs associated with models like Claude Opus or GPT.
However, you should note that this free tier is temporary. Once the promotional period ends, the API pricing will shift to $0.40 per million input tokens and $2.00 per million output tokens for Devstral 2.
Key Features
- Interactive Chat: You can chat naturally with the agent to break down complex tasks into manageable steps.
- Project-Aware Context: Mistral Vibe scans your project’s file structure and Git status automatically to understand the architecture before it suggests changes.
- Powerful Toolset: The agent can execute shell commands (
bash), manage files (read_file,write_file), and search code (grep) autonomously. - MCP Server Support: You can extend Mistral Vibe’s capabilities by configuring Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers in the configuration file.
- Slash Commands: You can use commands like
/for meta-actions and@for smart file path autocompletion. - Safety Controls: The agent features an approval mechanism for tool execution. You can also toggle an
--auto-approveflag for fully autonomous runs. - Multiple Built-in Agents: Choose from different agent profiles tailored for specific workflows.
Example Use Cases
- Legacy System Modernization: Refactor old codebases by describing the desired architecture. Mistral Vibe understands framework dependencies and can update multiple files to migrate from deprecated patterns to modern best practices.
- Cross-File Bug Fixes: Describe a bug that spans multiple files. The agent searches for the issue, understands how the files interact, and proposes fixes that maintain consistency across your codebase.
- Dependency Updates: Ask Mistral Vibe to update a library across your project. It finds all import statements, updates version numbers in package files, and adjusts code that relies on changed APIs.
- Code Exploration: Drop into a new codebase and ask questions about its structure. The agent maps out how components connect, explains design decisions, and helps you locate specific functionality.
- Automated Documentation: Generate README files, API documentation, or inline comments by having Mistral Vibe analyze your code and explain its purpose in natural language.
- Test Generation: Describe the functionality you need to test. Mistral Vibe examines your code, understands the expected behavior, and writes test cases that cover edge cases.
Case Studies
Simon Willison, a prominent voice in the AI engineering space, tested Mistral Vibe immediately after its release. He used the tool to generate a complete game from scratch.
Willison provided the prompt: “make me a space invaders game as HTML with three.js loaded from a CDN.” Vibe utilized its toolset to generate the necessary HTML and JavaScript files.
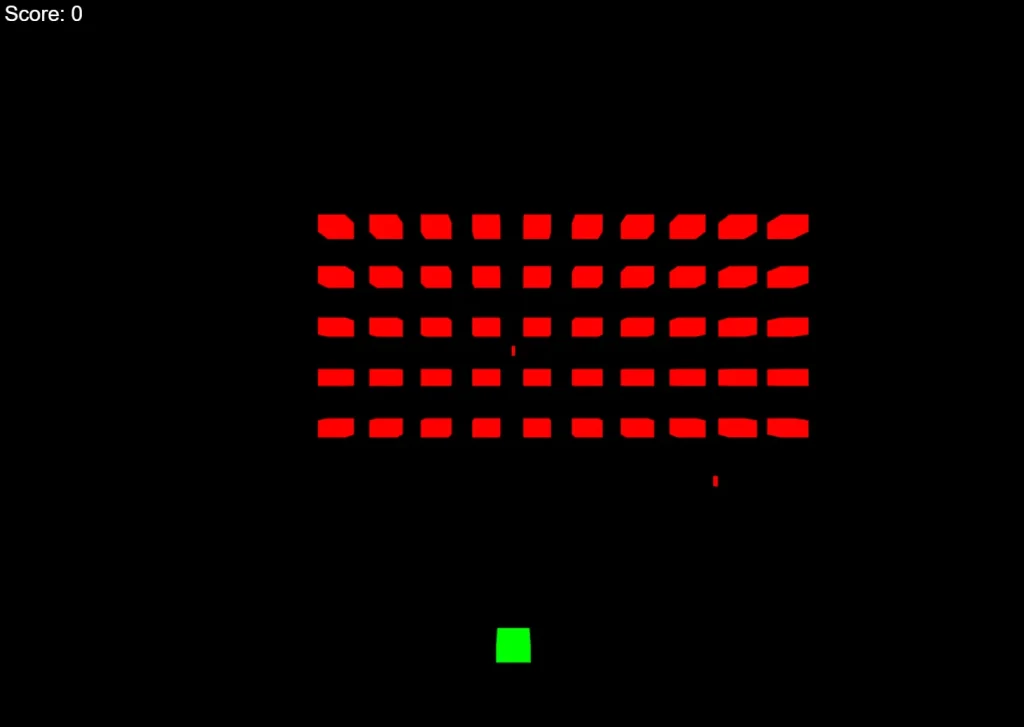
Willison noted that the tool “did OK,” which highlights that while the model is capable of scaffolding functional applications, it may still require human review for complex logic.
How to Use It
Installation
One-line install (Mac/Linux):
curl -LsSf https://mistral.ai/vibe/install.sh | bashUsing pip:
pip install mistral-vibeUsing uv:
uv tool install mistral-vibeInitial Setup
Navigate to your project’s root directory and run the vibe command to start. On first launch, Mistral Vibe creates a configuration file at ~/.vibe/config.toml and prompts you for your API key. The key gets saved to ~/.vibe/.env so you don’t need to enter it again. The setup takes less than a minute.
Interactive Mode
Type questions or instructions in natural language. Press Ctrl+J or Shift+Enter to add newlines in multi-line prompts.
Reference files by typing @ followed by the path. Mistral Vibe provides autocomplete suggestions as you type. Execute shell commands directly by prefixing them with !. This bypasses the AI and runs the command immediately.
Start Mistral Vibe with a prompt by passing it as an argument. Run vibe "Refactor the main function in cli/main.py to be more modular" to begin work on that specific task. The agent reads your files, analyzes the code, and suggests changes.
Auto-Approval Mode
Toggle auto-approval with Shift+Tab during interactive sessions. When enabled, Mistral Vibe executes all tool operations without asking permission. This speeds up workflows when you trust the operations. You can also start Mistral Vibe with the --auto-approve flag to enable this mode from launch.
Programmatic Mode
Run Mistral Vibe non-interactively for scripts and automation. Use vibe --prompt "Your task description" to execute a task and exit. This defaults to auto-approve mode since there’s no interactive session to confirm operations. Pipe input to Vibe or capture its output in shell scripts.
Configuration
Mistral Vibe reads configuration from ./.vibe/config.toml in your project directory. If that file doesn’t exist, it falls back to ~/.vibe/config.toml in your home directory. The TOML format lets you set the active model, customize tool permissions, and configure MCP servers.
Set your API key through environment variables (export MISTRAL_API_KEY="your_key"), the .env file in ~/.vibe/, or the interactive setup prompt. Environment variables take precedence over the .env file.
Custom System Prompts
Create custom prompts by adding Markdown files to ~/.vibe/prompts/. Set system_prompt_id = "my_custom_prompt" in your config to load ~/.vibe/prompts/my_custom_prompt.md. This lets you create specialized agents for specific tasks like security audits or code reviews.
Custom Agent Configurations
Build specialized agents by creating TOML files in ~/.vibe/agents/. Run vibe --agent redteam to load configuration from ~/.vibe/agents/redteam.toml. Agent configurations can disable certain tools, override permissions, and specify different system prompts.
MCP Server Integration
Add MCP servers to your config file to extend Mistral Vibe with external tools. The configuration supports HTTP endpoints, streamable HTTP for real-time updates, and stdio for local processes.
Each server needs a name, transport type, and connection details. HTTP servers can include custom headers and API key authentication.
Tool Filtering
Control which tools are active using enabled_tools and disabled_tools in your configuration. These fields support exact names like grep, glob patterns like serena_*, and regular expressions prefixed with re:. This helps limit what the AI can do in sensitive repositories or focus it on specific workflows.
Custom Vibe Home
Change where Mistral Vibe stores its files by setting the VIBE_HOME environment variable. Run export VIBE_HOME="/path/to/custom/vibe/home" to store configuration, API keys, custom agents, prompts, tools, and logs in a different location. This helps manage multiple Vibe installations or keeps work configurations separate from personal ones.
Pros
- Completely Free (Currently): The Devstral 2 model is free via Mistral’s API.
- Open and Transparent: The Apache 2.0 license allows for inspection, customization, and contribution.
- Architecture-Level Understanding: The model maintains context across your entire codebase. It can refactor patterns that span dozens of files without losing track of dependencies.
- Flexible Configuration: The TOML configuration system lets you customize every aspect of Mistral Vibe’s behavior. Set tool permissions, configure models, and create specialized agents for different tasks.
Cons
- Python 3.12+ Requirement: You need a recent Python version. Older systems might require Python installation or upgrades before using Mistral Vibe.
- UNIX Focus: Mistral Vibe is compatible with Windows but is officially designed for UNIX environments. Windows users might encounter compatibility issues or missing features.
- API Dependency: The agent requires an active internet connection and API access during the free period. Local model support exists but requires additional configuration.
- Context Window Limits: The 256K context window is large but finite. Extremely large codebases might exceed this limit and require careful prompting to work within constraints.
Related Resources
- Mistral Vibe GitHub Repo: Access the source code, issues, and documentation.
- Mistral Platform Console: Generate your API keys here to use the agent.
- Devstral 2 Model Card on Hugging Face: Technical specifications, benchmark results, and deployment instructions for the Devstral 2 model.
- SWE-bench Verified Benchmark: Read about the benchmark that evaluates coding models on real-world software engineering tasks.
- Best CLI AI Coding Agents: Discover the 7 best, open-source CLI AI coding agents.
FAQs
Q: Does Mistral Vibe require an internet connection?
A: Yes, Vibe needs internet access when using the Mistral API for Devstral 2. You can configure local models through the config.toml file to work offline, but this requires downloading and hosting the model weights yourself.
Q: How does Vibe compare to GitHub Copilot or Cursor?
A: Vibe operates as a terminal-native coding agent rather than an IDE extension. It excels at multi-file operations and autonomous task completion where you describe what you need and let the AI figure out the steps. Copilot and Cursor focus more on inline completions and suggestions as you type.
Q: Can I use Vibe with my own custom AI models?
A: Yes, the config.toml file lets you specify any model endpoint. You can point Vibe to local models running on your hardware, alternative API providers, or custom fine-tuned models.
Changelog
v2 (01/27/2026)
- Custom subagents: build specialized agents for targeted tasks. Deploy scripts, PR reviews, test generation – invoke them on demand.
- Multi-choice clarifications: Vibe asks before it acts. When intent is ambiguous, it prompts with options instead of guessing.
- Slash-command skills: load preconfigured workflows with /. Deploying, linting, generating docs – one keystroke.
- Unified agent modes: configure custom modes that combine tools, permissions, and behaviors. Switch contexts without switching tools.