CiteTrue is a free AI-powered citation verification tool that cross-references academic citations against millions of papers, journals, and books to detect fake or AI-generated references.
Academic integrity relies on accurate sourcing. Large Language Models (LLMs) frequently invent plausible-sounding but non-existent papers. You can use this tool to protect your work from citation fraud before submission or publication.
Features
- Batch verification: Process dozens or hundreds of citations with a single click.
- Multi-database cross-referencing: Searches across CrossRef, arXiv, CORE, OpenAlex, PubMed, ScienceDirect, SemanticScholar, OpenLibrary, Cambridge University, IEEE, Springer, Wiley, ACM, Elsevier, BMC, and ResearchGate.
- Automatic format correction: Fixes common formatting inconsistencies in your input, so you don’t need to manually standardize citations before verification.
- AI-generated detection: The system flags citations that appear to be fabricated by AI tools.
- Multiple input formats: Supports numbered citations, bullet-pointed lists, unnumbered references, and BibTeX entries.
Use Cases
- Pre-submission verification: Run your reference list through CiteTrue before submitting manuscripts to journals or conferences.
- Student paper review: Faculty members and advisors can verify citations in student theses, dissertations, and term papers.
- Peer review assistance: Reviewers can check suspicious citations in manuscripts they’re evaluating.
- Literature review validation: Researchers conducting systematic reviews or meta-analyses can verify that source papers actually exist and contain the claimed information.
- Collaborative research oversight: Research teams can verify citations from multiple contributors to ensure consistency and accuracy across large collaborative projects.
How to Use It
1. Visit the CiteTrue website and sign in using your Google account.
2. Paste your citations into the text field. CiteTrue accepts citations in various formats, and the AI automatically parses and separates individual references.
If the automatic parsing fails (which can happen with unusual formatting), reformat your citations using one of the supported structures. The tool currently accepts numbered citations (with brackets), bullet-pointed lists, unnumbered line-separated references, or BibTeX format.
[1] Jimmy Lei Ba, Jamie Ryan Kiros, and Geoffrey E Hinton. Layer normalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.06450, 2016.
[2] Dzmitry Bahdanau, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. CoRR, abs/1409.0473, 2014.
[3] Denny Britz, Anna Goldie, Minh-Thang Luong, and Quoc V. Le. Massive exploration of neural machine translation architectures. CoRR, abs/1703.03906, 2017.
• Jimmy Lei Ba, Jamie Ryan Kiros, and Geoffrey E Hinton. Layer normalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.06450, 2016.
• Dzmitry Bahdanau, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. CoRR, abs/1409.0473, 2014.
• Denny Britz, Anna Goldie, Minh-Thang Luong, and Quoc V. Le. Massive exploration of neural machine translation architectures. CoRR, abs/1703.03906, 2017.
Jimmy Lei Ba, Jamie Ryan Kiros, and Geoffrey E Hinton. Layer normalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.06450, 2016.
Dzmitry Bahdanau, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. CoRR, abs/1409.0473, 2014.
Denny Britz, Anna Goldie, Minh-Thang Luong, and Quoc V. Le. Massive exploration of neural machine translation architectures. CoRR, abs/1703.03906, 2017.
@article{ba2016,
author = {Ba, Jimmy Lei and Kiros, Jamie Ryan and Hinton, Geoffrey E},
title = {Layer normalization},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.06450},
year = {2016}
}
@article{bahdanau2014,
author = {Bahdanau, Dzmitry and Cho, Kyunghyun and Bengio, Yoshua},
title = {Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/1409.0473},
year = {2014}
}
@article{britz2017,
author = {Britz, Denny and Goldie, Anna and Luong, Minh-Thang and Le, Quoc V.},
title = {Massive exploration of neural machine translation architectures},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/1703.03906},
year = {2017}
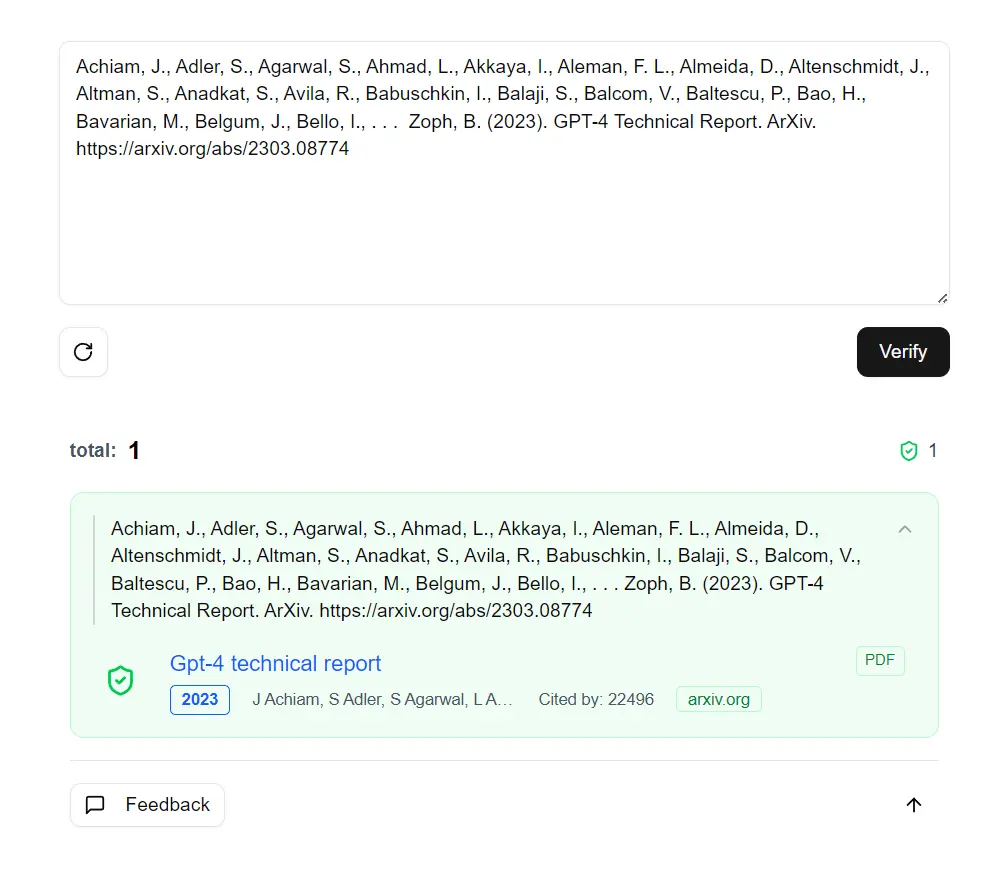
}3. Click the “Verify” button. CiteTrue processes your citations and returns results within seconds, even for large reference lists.
4. If verified, the tool shows publication year, citation count, publishing platform, and provides a direct link to read the original document.
Pros
- Cost: The tool is completely free to use.
- Speed: It verifies large lists of references in seconds.
- Correction: It fixes formatting errors automatically during the check.
Cons
- Account Requirement: You must log in with a Google account to access the features.
- Input Sensitivity: Poorly formatted text blocks may require manual adjustment if the AI fails to split them.
Related Resources
- CrossRef: The official DOI registration agency where you can manually verify individual DOIs and access publication metadata.
- Google Scholar: Search engine for academic literature that helps you find original sources and check citation counts.
FAQs
Q: Why do I need to verify citations generated by AI?
A: AI models like ChatGPT often “hallucinate” citations. They create realistic-looking titles and author lists that do not actually exist. CiteTrue checks these against real databases to prevent academic misconduct.
Q: Does CiteTrue work with citations in languages other than English?
A: CiteTrue can process citations in multiple languages since it searches across international academic databases. The verification accuracy depends on whether the cited work exists in one of the connected databases.
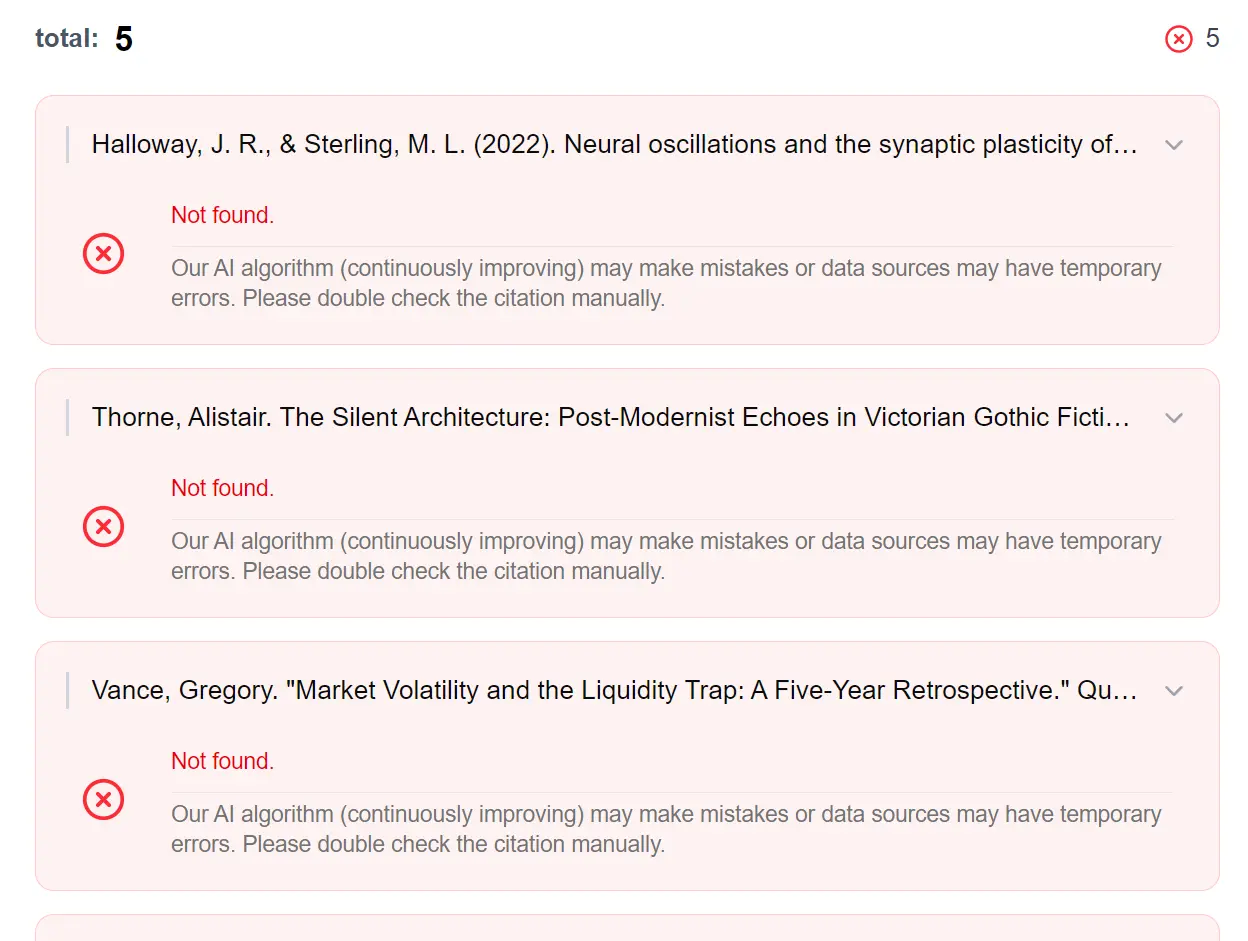
Q: What happens if CiteTrue can’t verify one of my citations?
A: An unverified citation doesn’t automatically mean it’s fake. The reference might exist in a database CiteTrue doesn’t access, or it could be a recent publication that hasn’t been indexed yet. You’ll need to manually verify these citations through the original publisher or institutional library.
Q: Can I use CiteTrue to verify citations in my thesis?
A: Yes. Thesis and dissertation citations work the same way as any other academic document. Paste your reference list into CiteTrue before submitting to your graduate school to catch any problematic citations.
Q: How accurate is the AI-generated citation detection?
A: CiteTrue uses pattern recognition to flag citations that match characteristics of AI-generated text. This includes unusual formatting, impossible author combinations, or journal names that don’t exist in any database.
Q: Can I verify just a few citations or do I need to upload my entire reference list?
A: You can verify any number of citations. The tool works equally well for checking one suspicious reference or processing a complete bibliography of hundreds of citations.