GitHub Repo Visibility Analyzer is a free AI-powered audit tool that examines your repository and provides actionable topic tag recommendations to improve its visibility across GitHub searches, Google results, and large language model responses.
Developers often spend weeks building a library or framework, but spend zero time on how people find it. You might have clean code, but if your repository lacks the right metadata, it sits buried on page ten of the search results.
This tool acts like an SEO consultant specifically for your GitHub projects. It tells you exactly which tags you are missing, which ones are useless, and how to position your repo so other developers actually see it.
Features
- Smart Topic Tag Analysis: Examines your current topic tags and identifies missing opportunities based on search volume and competition levels.
- Search Ranking Insights: Shows where your repository appears in GitHub topic pages and reveals if you’re buried below thousands of star-heavy competitors.
- Comprehensive Scoring System: Provides separate scores for Reach (0-100), Competition (0-100), Intent (0-100), and Hook (0-100) to help you understand your visibility from multiple angles.
- Actionable Recommendations: Delivers a personalized audit report with specific issues to fix, ranked by impact on discoverability.
- AI-Generated Tag Suggestions: Produces hundreds of relevant topic tags based on your repository’s content, tech stack, and use cases.
- Cross-Platform Visibility: Analyzes how your repo performs not just on GitHub, but also in Google search results and AI model responses.
- Topic Page Performance Tracking: Reveals your ranking position for each topic tag and shows how many competitors you’re up against.
- Historical Data Insights: Displays repository statistics like star count, last push date, and topic usage patterns.
Use Cases
- Open source maintainers: Projects seeking contributors need maximum visibility to attract developer attention.
- New library launches: Recently published packages can quickly gain traction by appearing in relevant topic searches.
- Portfolio projects: Developers showcasing their work want their repositories easily discoverable by potential employers or collaborators.
- Enterprise projects: Internal tools or company open source initiatives need to be found by the right teams and stakeholders.
Case Study: Auditing ‘awesome-claude-code’
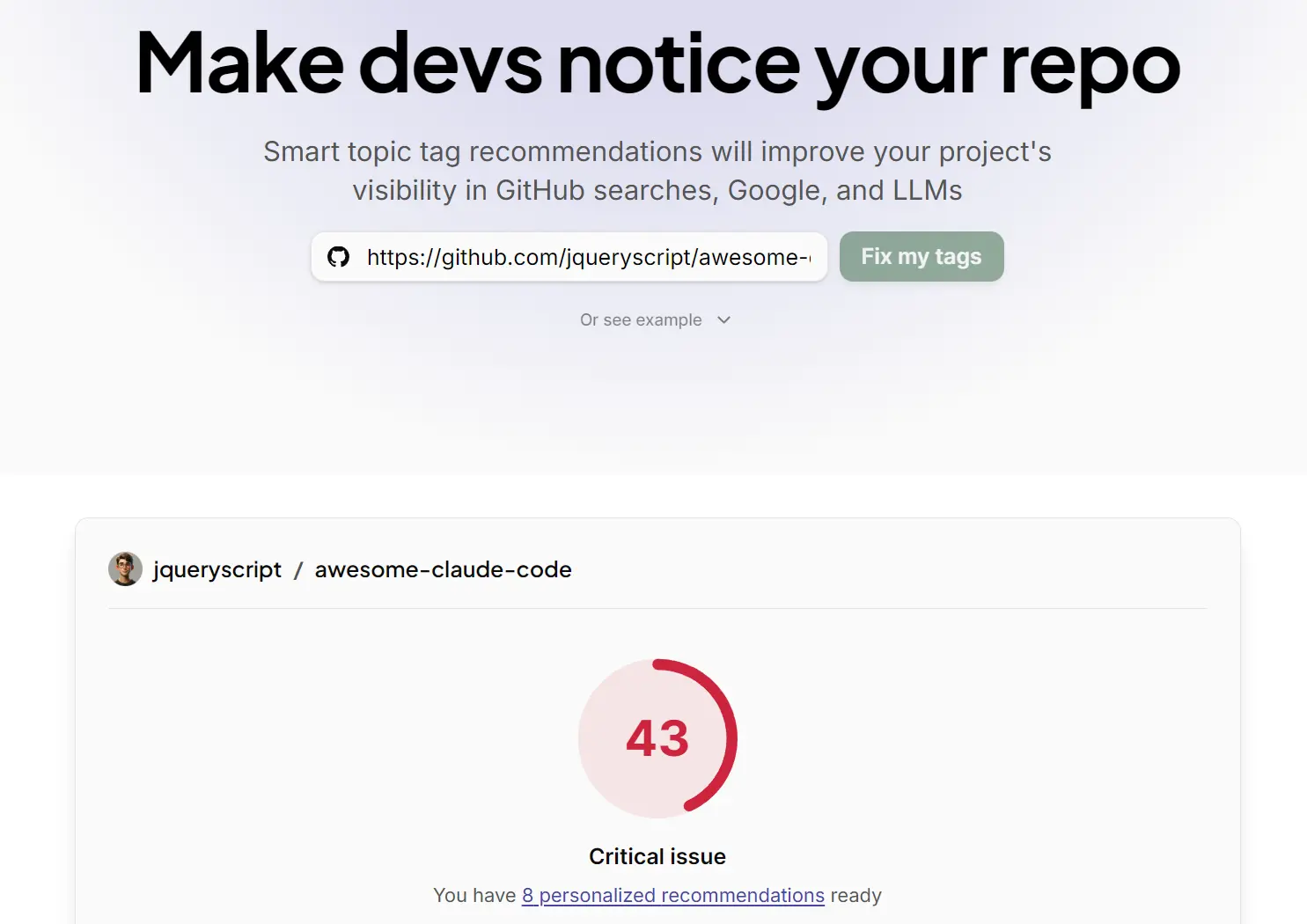
I recently used this tool to analyze my own repository, awesome-claude-code. This is a curated list of resources for Anthropic’s Claude Code. Despite having 66 stars, I felt the traffic was lower than it should be given the current hype around AI agents.
I plugged the URL into the analyzer. The process took about a minute. The tool gave me a blunt reality check: a score of 43 out of 100.
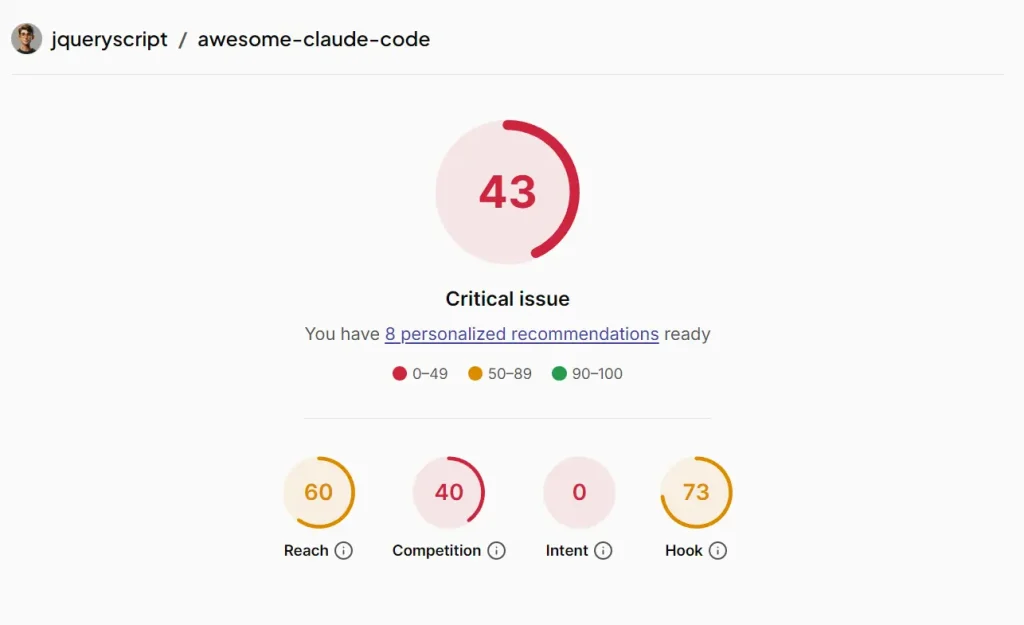
Here is what the audit revealed:
- My tags were too niche: I was ranking #1 for “awesome-list” (singular), but I completely missed “awesome-lists” (plural), which has significantly more traffic.
- I missed high-volume keywords: The AI suggested 180 tags. I realized I hadn’t included obvious ones like “agentic-coding,” “ai-workflows,” or even “anthropic-claude.”
- My “Hook” was strong, but “Intent” was zero: People who found the repo liked it (73 Hook score), but very few people were finding it in the first place because my search intent keywords were missing.
The tool gave me 8 specific fixes. It told me to remove “beta-feature” tags that were wasting space and replace them with “agents” and “automation.” After applying just the top 5 recommended tags, my visibility on the “Claude” topic page improved.
How to Use It
1. Visit the GitHub Repo Visibility Analyzer and paste your GitHub repository URL.
2. Click “Fix My Tags,” and the AI begins scanning your repository immediately. This process typically takes 60-90 seconds as the tool examines your current tags, analyzes your repository content, checks your rankings on topic pages, and compares you against competitors.
3. Review your overall scores once the analysis is complete. You’ll see four separate metrics: Reach measures your potential audience size, Competition shows how difficult your current topics are to rank for, Intent indicates how well your tags match what developers actually search for, and Hook evaluates how compelling your repository appears in search results.
4. Examine the detailed audit results below the scores. The tool breaks down issues into categories: things you need to add (like popular tags used by 5,000+ repositories), things you should adopt (established tags with 1,000+ repositories), and things you should remove (tags that don’t contribute to discoverability like “beta-feature” or “2027”). Each recommendation explains why it matters.
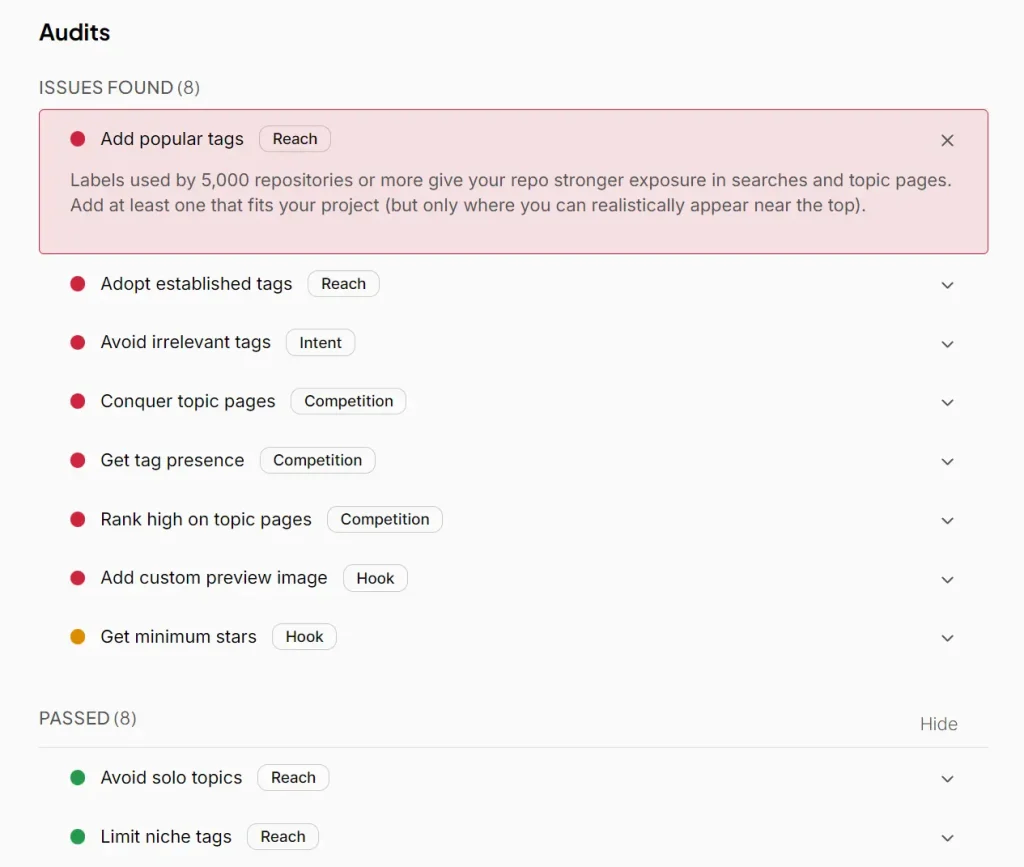
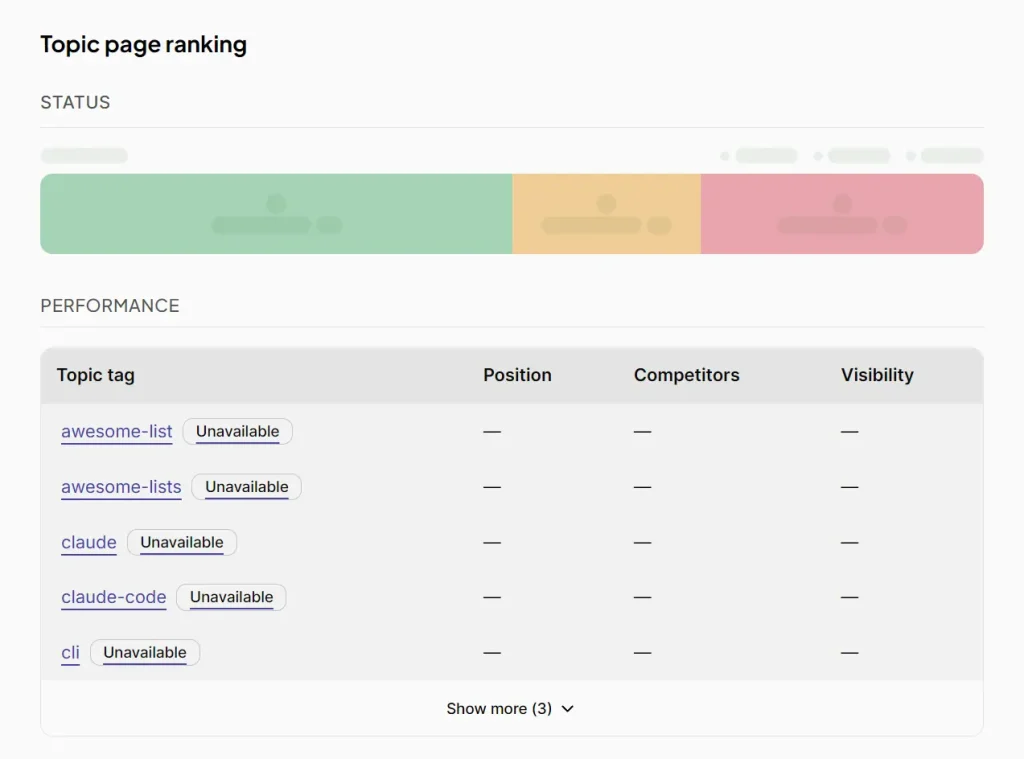
5. Check the “Data and Insights” tab to see where you currently rank for each of your existing topic tags. This section shows your position on topic pages, how many competitors you’re facing, and your visibility score for each tag. If you see “Unavailable” for a tag, it means GitHub hasn’t indexed your repo for that topic yet.
6. Scroll down to the AI-generated tag suggestions at the bottom. The tool typically generates 100-200 relevant tags based on your repository’s actual content. These aren’t random. They’re selected based on your code, README, and project structure. Copy the tags that accurately describe your project.
7. Navigate to your GitHub repository and click “Settings”, then scroll to the “Topics” section. Add the recommended tags one by one. GitHub allows up to 20 topics per repository, so prioritize tags where you can realistically rank in the top positions rather than choosing only high-competition terms.

8. Wait 24-48 hours for GitHub to re-index your repository with the new tags, then run the analyzer again to measure your improvement. You’ll see better scores and more “passing” audit checks.
Pros
- Completely free: No tier limitations or usage restrictions for the analysis service.
- Actionable data: Provides specific tag recommendations rather than general advice.
- Contextually aware: Considers both popularity and ranking feasibility when suggesting tags.
- Immediately implementable: Changes can be made directly through GitHub’s interface.
Cons
- No historical tracking: Cannot compare current performance with past metrics or track improvements over time.
- Limited to public repos: Doesn’t work with private repositories that might also benefit from better organization.
- Manual implementation: Requires you to manually update your repository settings based on the recommendations.
Related Resources
- GitHub Topics Documentation: Official guide on how to add and manage topics on your GitHub repositories.
- GitHub Search Syntax Guide: Learn advanced search operators to understand how developers find repositories like yours.
- Open Source Guide to Marketing Your Project: Comprehensive resource on attracting users and contributors to open-source projects beyond just tags.
- GitHub Traffic Insights: Use GitHub’s built-in analytics to track how people are discovering and interacting with your repository.
FAQs
Q: How often should I re-analyze my repository?
A: Run the analyzer after major updates to your project—like adding new features, changing your tech stack, or shifting your target audience. Tags that were optimal at launch might not match what your repository has evolved into. I’d suggest quarterly audits as a baseline, with additional checks after significant changes. If you’re actively trying to grow your project, monthly reviews help you stay on top of trending topics in your space.
Q: What’s the difference between “reach” and “competition” scores?
A: Reach measures the total potential audience for your current tags: how many people search for those topics. Competition measures how hard it is to rank well for those tags based on how many other repositories use them and how many stars those competitors have. You want high reach with manageable competition. A tag with 10,000 searches but 50,000 competitors isn’t as valuable as one with 2,000 searches and 500 competitors.
Q: Will the AI-generated tags work for any programming language?
A: The tool analyzes repositories across all languages and generates appropriate tags based on your actual code and documentation. If your repo lacks documentation, the AI has less context to work with and might produce more generic suggestions.