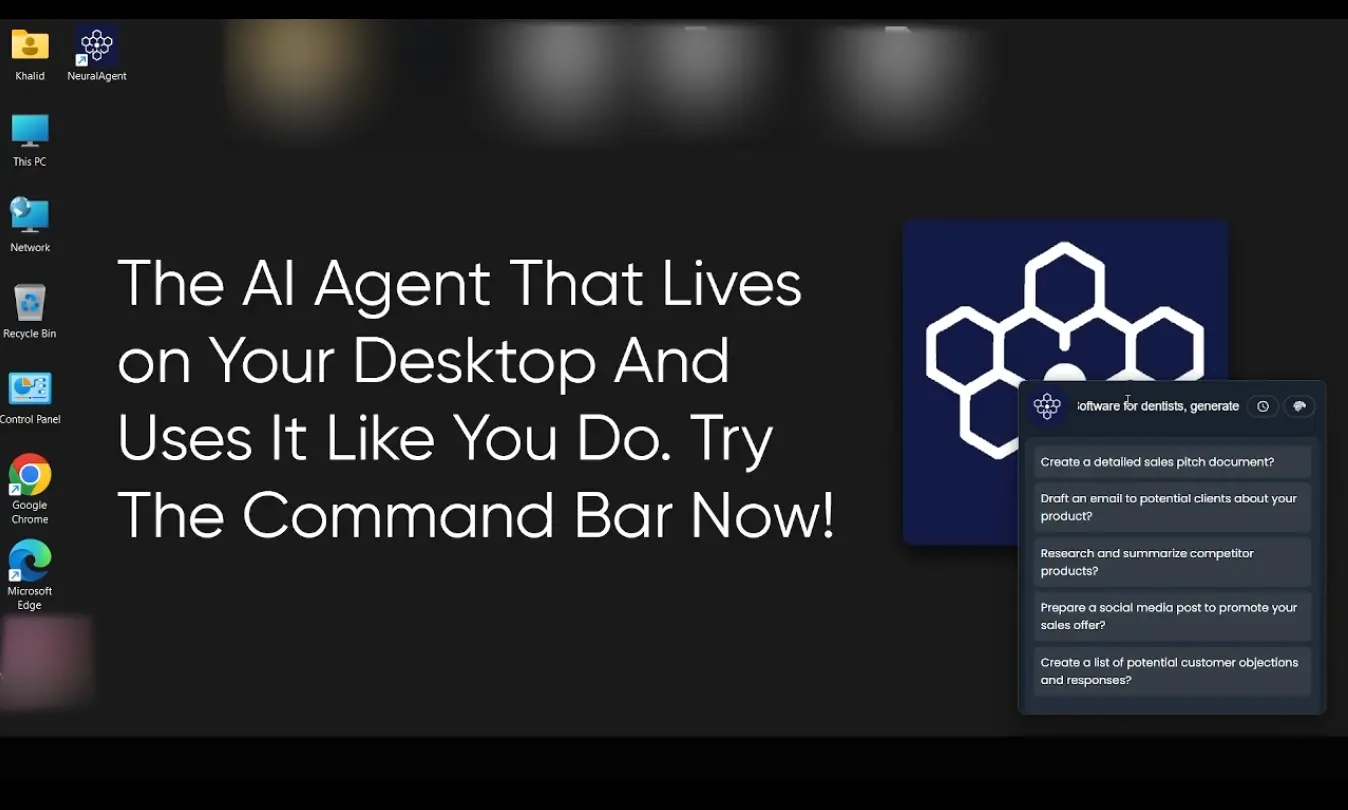
NeuralAgent is a free, open-source, AI-powered desktop automation agent that controls your computer like a human would.
It lives on your desktop, types, clicks, navigates the browser, fills out forms, sends emails, and performs tasks automatically using modern LLMs, all powered by a fast, extensible, and open architecture.
Features:
- Desktop automation with PyAutoGUI: Controls mouse movements, keyboard inputs, and screen interactions across any application on your desktop.
- Background browser automation: Runs browser tasks in the background through WSL (currently Windows-only), allowing you to continue working while automation happens behind the scenes.
- Multi-model AI support: Compatible with Claude, GPT-4, Azure OpenAI, Bedrock, Ollama, and Gemini, so you can use your preferred language model.
- Modular agent architecture: Includes specialized agents for planning, classifying tasks, suggesting improvements, generating titles, and executing computer actions.
- Multimodal capabilities: Processes both text commands and visual information, enabling more sophisticated task understanding.
- Modern tech stack: Built with FastAPI backend, Electron desktop app, and React frontend for a responsive user experience.
- Cross-platform compatibility: Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux, though background automation is currently limited to Windows.
- Local operation: Runs entirely on your machine without requiring cloud dependencies for core functionality.
See It In Action
Use Cases
- Research and documentation: The tool can navigate multiple websites, extract relevant data, and organize findings into readable formats.
- Form filling and data entry: Process batches of forms across different applications, populate fields with data from spreadsheets or databases, and submit completed forms automatically.
- Email management and outreach: Compose and send personalized emails based on templates, manage follow-up sequences, and organize inbox responses according to predefined criteria.
- Content creation workflows: Navigate content management systems, upload media files, format text according to style guidelines, and publish content across multiple platforms.
- Development task automation: Open development environments, execute common coding tasks, run test suites, and manage file operations across projects.
How to Use It
1. To get started, make sure you have Python (3.9+), PostgreSQL (13+), and Node.js (18+) installed.
2. My best advice is to open two separate terminal windows before you do anything else. You will use one for the backend server and the other for the desktop application.
Terminal 1: Backend Setup
In your first terminal, you will get the backend server running. This is the core engine that processes your commands.
Get the code by cloning the NeuralAgent repository from GitHub. Then, navigate into the backend directory. It’s a good practice to create and activate a Python virtual environment to keep the project’s dependencies separate from your system’s.
cd backend
python -m venv venv
# On macOS/Linux, activate with:
source venv/bin/activate
# On Windows, use:
venv\Scripts\activateWith the virtual environment active, install all the necessary Python packages using the requirements file.
pip install -r requirements.txtNext, you need to set up your database. Make sure PostgreSQL is running and create a new, empty database for NeuralAgent.
After that, you’ll configure the application’s environment variables. Copy the example .env.example file to a new file named .env.
Open this new .env file and fill in your database connection details: DB_HOST, DB_PORT, DB_DATABASE, DB_USERNAME, and DB_PASSWORD. You also need to generate a unique random string for the JWT_SECRET. If you plan to use a specific AI model provider like OpenAI or Anthropic, this is where you will add your API keys.
With the configuration in place, run the database migrations. This command automatically sets up the necessary tables in the database you created.
alembic upgrade headFinally, start the backend server. Leave this terminal running, as the desktop app needs to connect to it.
uvicorn main:app --reload --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000Terminal 2: Frontend (Desktop App) Setup
Now, switch over to your second terminal. Here, you’ll set up and launch the frontend application that you interact with.
Navigate to the desktop directory from the project’s root folder and install the necessary Node.js dependencies.
cd desktop
npm installThe desktop application contains a React app that also needs its own dependencies. Navigate into the neuralagent-app directory and run the installation command again.
cd neuralagent-app
npm installLike the backend, the frontend has an environment file you need to create. Copy the .env.example to a new .env file. For a standard local setup, the default values should work fine.
The final piece of the setup is the local AI agent daemon. This is a small Python service that is responsible for controlling your mouse and keyboard. Go back to the desktop root directory, then into the aiagent folder. It needs its own, separate Python environment.
cd ../aiagent
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # Or venv\Scripts\activate on Windows
pip install -r requirements.txt
deactivateNow you are ready to launch the application. Return to the main desktop directory and run the start command.
cd ..
npm startThis will compile the application and launch the NeuralAgent window on your screen. With the backend running in your first terminal and the frontend active, you can start giving commands to your new desktop AI assistant.
Pros
- Real desktop interaction: NeuralAgent actually controls your computer instead of just providing suggestions.
- Multiple AI model options: Choose the right model for each specific task based on your needs and budget.
- Open-source and free: No hidden costs or premium features locked behind paywalls.
- Cross-platform compatibility: Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux for most features.
- Modular architecture: Different agents handle specialized tasks, making the system more efficient.
- Local processing: Your data stays on your machine rather than being sent to third-party servers.
Cons
- Technical setup required: Installation involves multiple components that might challenge less technical users.
- Background automation limited to Windows: Mac and Linux users can’t run browser tasks in the background yet.
- Potential for errors: Since it controls your mouse and keyboard, mistakes could cause unintended actions.
- Resource intensive: Running both the Electron app and AI models simultaneously uses significant system resources.
- Limited error recovery: If NeuralAgent gets stuck, you often need to restart the process manually.
Related Resources
- Official NeuralAgent Website: Access documentation, community discussions, and official updates about the project.
- NeuralAgent GitHub Repository: Download source code, report issues, and contribute to development.
- NeuralAgent Discord Community: Connect with other users, get help with setup issues, and share automation use cases.
- PyAutoGUI Documentation: Learn about the underlying automation library that powers NeuralAgent’s desktop control capabilities.
- FastAPI Documentation: Understand the backend framework used in NeuralAgent’s architecture for API development.
- Electron Framework Guide: Explore the desktop application framework that provides NeuralAgent’s user interface.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between foreground and background automation?
A: Foreground automation takes over your computer’s controls; you can see the mouse moving and text being typed. Background automation (currently Windows-only) performs tasks in a browser behind the scenes, so it doesn’t interrupt your own work.
Q: Can NeuralAgent work without an internet connection?
A: NeuralAgent can run locally, but it requires internet access to communicate with AI model APIs like OpenAI or Anthropic. If you use Ollama with local models, you can achieve offline operation, though setup complexity increases significantly.
Q: How does NeuralAgent compare to tools like Zapier or n8n for automation?
A: NeuralAgent focuses specifically on desktop application control and can interact with any software installed on your computer. Zapier and n8n excel at web service integrations and API connections but cannot control desktop applications or perform mouse and keyboard actions.
Q: Can I customize NeuralAgent’s behavior for specific applications?
A: Yes, the modular architecture allows customization of individual agents and their behavior. You can modify the source code to add application-specific logic or create custom workflows for your particular use cases.